USAID has recently released their June 2016 “Acting On The Call: Ending Preventable Child And Maternal Deaths Report”. This report’s main focus is to address equity in USAID’s 24 priority countries. With detailed charts and briefs of the improvements made this year, there is also a series of suggestions in which programs can provide new solutions to better approach equity.
The Hunger Project works with 8 of USAID’s 24 priority countries. To provide THP supporters with a more relatable guideline on the report , below will be a mix of visuals and short briefs of each THP countries yearly improvement and what still needs to be done.
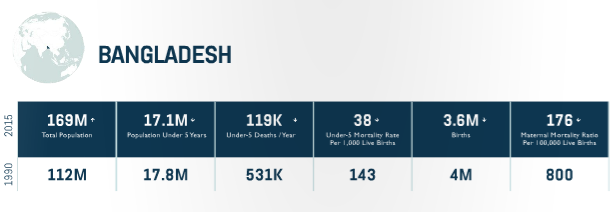
Progress
-The National Fistula Strategy was approved to reduce the burden among those living with fistula.
-Two hundred dedicated Severe Acute Malnutrition units were established in public health facilities.
-A Memorandum of Understanding between Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, and Bangladesh Garment Manufacturing Exporters Association was signed to expand FP services to reach garment factory workers in over 40 garment factories.
Equity Approach
-Supporting increased antenatal care (ANC) for women through CHW outreach, particularly to the poorest women.
-Reducing gender- based violence among the most vulnerable populations.
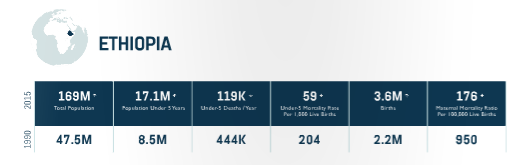
Progress
-USAID provided expertise and assistance to the government of Ethiopia to develop, revise, and implement key strategies and guidelines.
-USAID contributed to the roll out of community-based newborn care in 18 zones/196 districts in rural areas, and partnered with the GoE and the Ethiopian Pediatric Society to develop a comprehensive proposal to implement the “Helping Babies Survive’ program in 180 hospitals.
Equity Approach
-Collaborating with the GoE to improve the health of Ethiopians focused on the most vulnerable women,girls,newborns, and children under the age of five.
-Supporting expansion of community-based health insurance schemes that reached 6.5 million people this year.
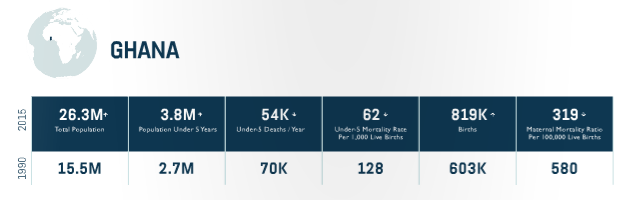
Progress
-Incorporated chlorhexidine and antenatal corticosteroids into the Essential Medicines List of Ministry of Health .
-Developed costed implementation plan for increasing quality family planning services.
Equity Approach
-Ensuring services in some of the most undeserved areas of the country-specifically the Northern region- to address lagging health indicators.
-Rolling out the national policy for Community-based Health Planning Service zones , which serve as the first point of care in many communities.
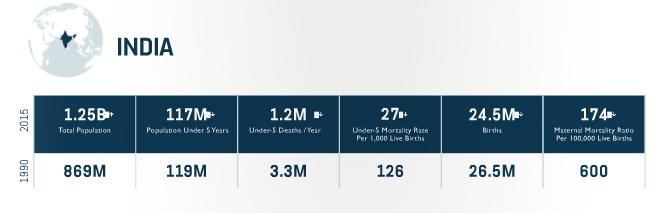
Progress
-Established quality improvement teams in health facilities across High Priority Districts, resulting in a 13 percent decline in neonatal mortality at USAID supported facilities.
-Supported the Government of India (Gol) in hosting the third global Call to Action Summit, where the 2015 Acting on the Call report was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Equity Approach
-Supporting the National Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A) Unit that monitors the progress in improving key health outcomes in 184 High-Priority Districts across the country.
-Collaborating with the private sector to help it comply with, and take advantage of , a recent law mandating certain companies to invest in Corporate Social Responsibility activities.
Progress
-Conducted training of trainers on postnatal care. Postnatal care registers were printed out and distributed to all facilities in the country to enable better monitoring of quality service provision for newborns.
-Integrated family planning and immunization services, (a recognized high-impact practice) wee rolled out in two districts.
Equity Approach
-Improving equity and efficiency in the delivery of quality Essential Health Package services through a human rights-based approach.
-Outreach, including mobile clinics, to overcome barriers to serving hard to reach populations.

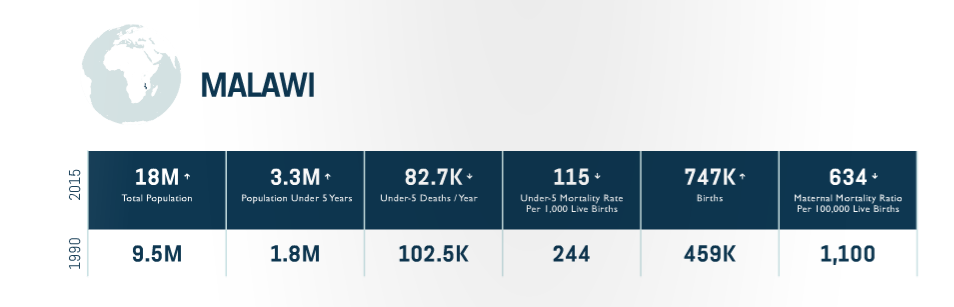
Progress
-The Ministry of Health adopted a National Behavioral Change Strategy for Nutrition.
-The National Fortification Policy has been adopted and includes mandatory fortification of five key staple foods, and the phased roll out of a national micro nutrient powder program.
Equity Approach
-Expansion of high-impact, evidence-based interventions, including; iCCM to address the major diseases responsible for under-5 deaths, including recognition of danger signs’ misoprostol for the prevention of postpartum hemorrhage; and chlorhexidine during newborn cord care.
-Focusing maternal health service on adolescents, with programs aiming to increase both the capacity of communities and the responsiveness of the Ministry of Health to be to meet the growing needs of this sizable population of young mothers.
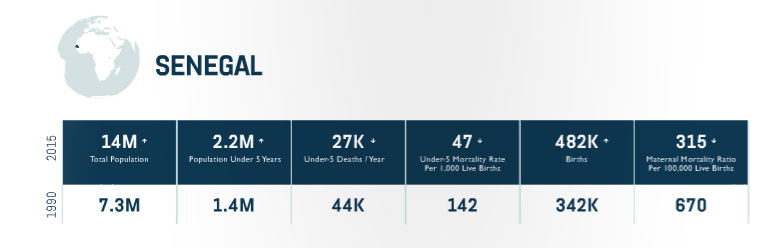
Progress
-Provided technical assistance to the Ministry of Health to elaborate, validate, and disseminate a national nutrition strategic plan and national family planning framework strategy.
-USAID has increased the availability of equipment for newborn care in 80 percent of facilities in 10 regions, scaled up availability of misoprostol for postpartum hemorrhage to over 979 health huts, and scaled up use of chlorhexidine for newborn sepsis to over 1,200 health huts.
Equity Approach
-Working to reduce inequities and reach the most vulnerable in line with the GoS vision in the Plan Senegal Emergent of “a Senegal where all individuals, all households and all communities enjoy universal access to promotional, preventive, curative health services of quality, without any form of exclusion.
-Supporting the creation and expansion of mutuelles, community-based health insurance, a cornerstone of the GoS effort to ensure access to essential health services throughout the country.
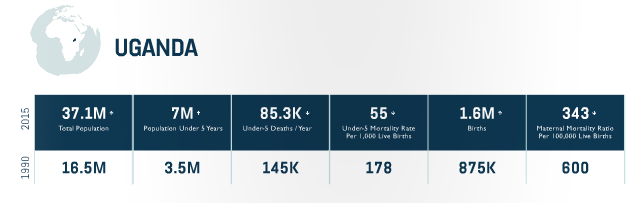
Progress
-Enhanced services in the Southwest region through the regional integrated health program, which incorporated support for maternal and child health and family planning to improve overall health outcomes.
-USAID has been included in the GFF and is supporting completion of the costed RMNCAH plan, which will improve coordination of RMNCAH.
Equity Approach
-Developing integrated programming in regions with district-wide support to scale-up service delivery access points and thereby reduce health inequities.
-Improving access to care across programs through:
-Outreach service delivery(in addition to facility service support)
-Targeting populations with high burden of disease/death (e.g. youth, specifically girls).


